Edge Functions
Edge functions let you define custom logic to run on the same nodes as your database files for ultra-fast performance.
You can write edge functions directly in the SQLite Cloud dashboard using JavaScript, TypeScript, or SQL. Importing modules is not currently supported.
Edge functions can be called remotely over HTTP or Websockets via API, or triggered by database events via SQLite Cloud Webhooks. Each function runs in an isolated environment using the Bun runtime.
Turning on linearizable reads ensures strong consistency, but may introduce some latency. When eventual consistency is sufficient, we recommend leaving linearizable reads off.
Getting Started
Use the Edge Functions panel to effortlessly create, deploy, and test Edge Functions directly in the SQLite Cloud dashboard.
The editor allows you to choose the language of your function — JavaScript, TypeScript, or SQL — and connect it to the database of your choice.
Once deployed, the function can be tested immediately in the dashboard or invoked externally through its Function URL.
Note:
Functions should return a JSON-serializable object with a data field:
return {
data: {
// your return object
}
}
Enabling linearizable reads guarantees strong consistency but may introduce additional latency.
For most cases, we recommend keeping it disabled to benefit from lower response times.
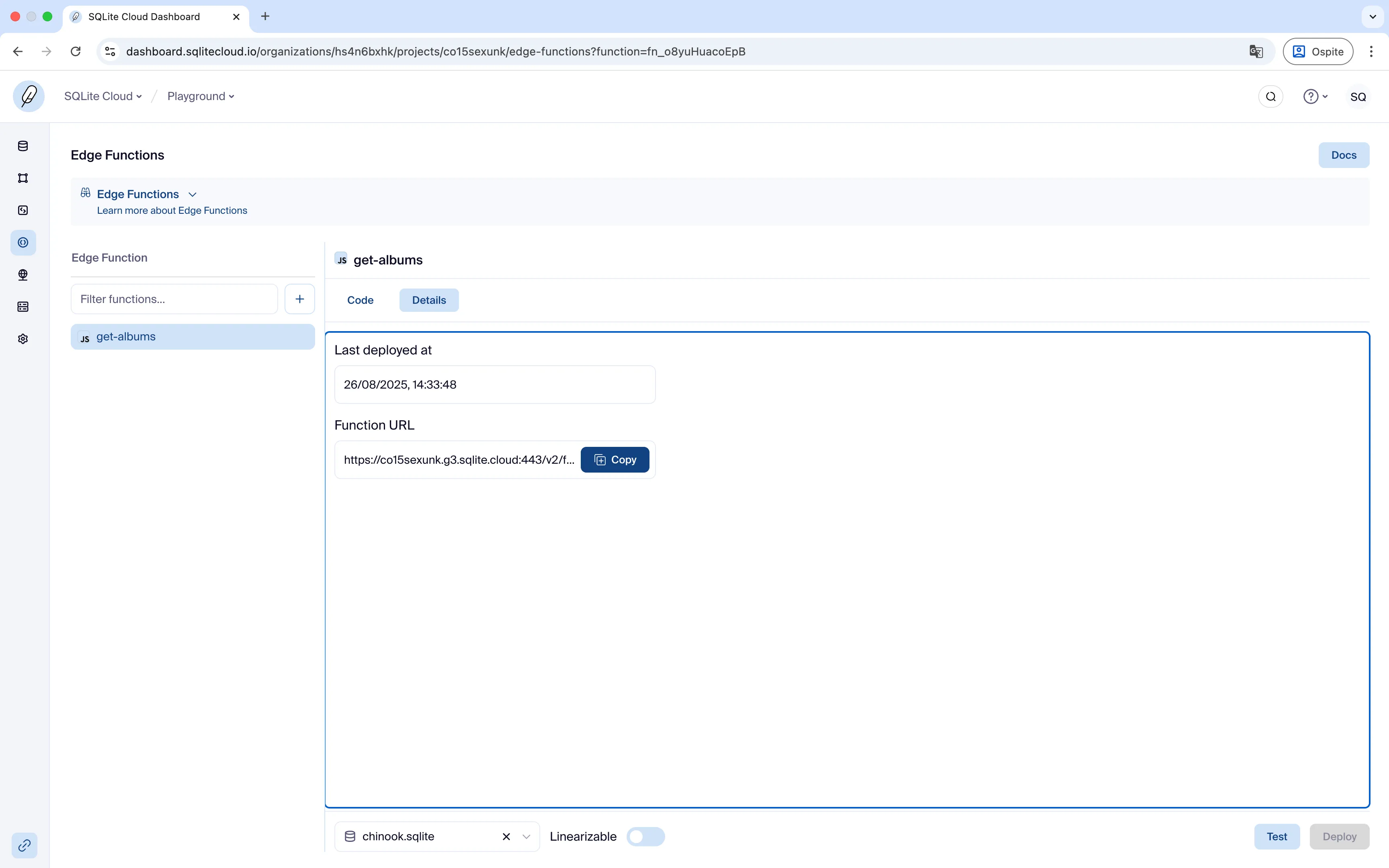
Function Details
In the Details tab you will find key information about your function, including:
- The last deployment date and time
- The Function URL, which you can use to call the function from external applications
Authorization
Edge functions that access your SQLite databases must be authorized via API key.
An API key must be sent in the request url as a query parameter (?apikey=YOUR_API_KEY) or as an attribute in the request body ({ apikey: YOUR_API_KEY }).
Execution
Edge functions can be called via HTTP GET and POST methods. You can pass additional values to your edge function in two ways:
- Query parameters: Accessible via
request.params - Request body: Accessible via
request.data
Guides
Interacting with your Database
Use the global connection object to access and manipulate your database.
const customers = await connection.sql`SELECT * FROM customers;`
return {
data: customers
}Select the database you would like to access from the “Database” dropdown, or select the database you want to use in your SQL query with the USE command.
const customers = await connection.sql`USE DATABASE chinook.sqlite; SELECT * FROM customers;`;
return {
data: customers
}Storing and Accessing Environment Variables
Environment variables can be accessed and stored with the ENV command. ENV variables are stored in the server settings file and are project-specific. Use the following commands to set and read values in your server settings file:
- LIST ENV
- SET ENV key VALUE value
- GET ENV key
- REMOVE ENV key
You can also add environment variables in the UI by navigating to the “Environment Variables” section and clicking the “Create” button.
Handling Errors
In case of error we return an HTTP error code and a JSON with the error message. Manually throwing an error in your code results in a 500 response. You may also return an error.
Examples
Assigning and Notifying a Support Rep on User Sign up
// Get secret from database
const slackWebhookEndpoint = await connection.sql`GET ENV slack_webhook_endpoint`;
// Get record sent in body via webhook
const content = request.data;
const database = content.database;
const primaryKey = content.data[0];
const newCustomer = await connection.sql`USE DATABASE ${database}; SELECT * FROM customers WHERE CustomerId = ${primaryKey};`;
// Sample business logic - assign and notify support rep
// Get reps from database
const reps = await connection.sql`SELECT id, name, country FROM reps`;
const rep = reps.find(({ country }) => country === newCustomer.country.toLowerCase());
// Define helpers to assign and notify
const assignRep = async (repId, customerId) => await connection.sql`UPDATE customers SET SupportRepId = ${repId} WHERE CustomerId = ${customerId}`;
const notifyRep = async (repName, customer) => {
const message = `@${repName}: New User Sign Up - ${JSON.stringify(customer)}`
try {
await fetch(slackWebhookEndpoint, { body: JSON.stringify({ text: message }), method: 'POST', 'Content-type': 'application/json' });
} catch (err) {
await fetch(slackWebhookEndpoint, { body: JSON.stringify({ text: err }), method: 'POST', 'Content-type': 'application/json' });
}
}
// Call async functions
await assignRep(rep.id, newCustomer.id);
await notifyRep(rep.name, newCustomer);
return {
data: 'OK'
}